- (888) 4000-2424
- admin@gmail.com
A data center located in Raton plays a strategically important role by reducing network latency and strengthening power availability along a critical corridor that connects major population and infrastructure hubs in the central and southwestern United States. Positioned between markets such as Denver, Albuquerque, and Dallas, a Raton-based data center shortens physical network paths, resulting in faster data transmission, improved application performance, and more resilient routing for cloud, enterprise, and edge workloads. In addition, the region’s access to transmission infrastructure and comparatively unconstrained power capacity enables scalable, reliable energy delivery, helping to relieve pressure on overbuilt metro data center markets while improving redundancy and continuity for networks that traverse this key geographic gateway.
| Municipality | Key Strengths |
| Pueblo, CO | Low-cost land, enterprise zone incentives, industrial power capacity |
| Raton, NM | Opportunity Zone, vacant Kmart & substation, rural job credits |
| Colorado Springs/Castle Rock, CO | Low electric rates, tech workforce, state data center credit |
| Santa Fe, NM | Vacant Kmart, excellent climate, proximity to ABQ |
| Albuquerque, NM | Existing data market, brownfields, full suite of NM incentives |
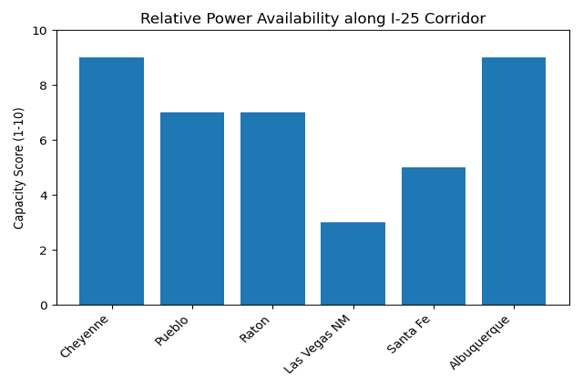
“Raton stands out because due to their decommissioned 115 kV substation; that legacy infrastructure provides about 20 MW of immediate capacity and makes it relatively easy to scale up to roughly 50 MW with targeted investment.”

Colorado registered over 90k EVs by end‑2023; EV adoption is surging across the region.
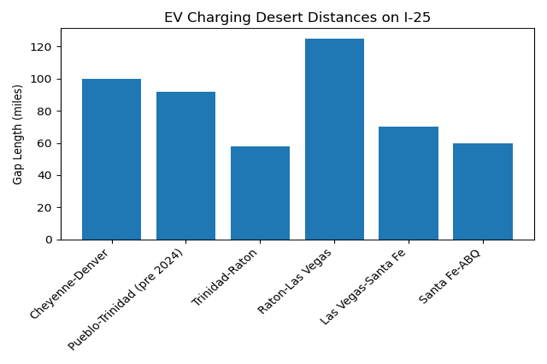
The most underserved segments on I‑25 are Cheyenne to Denver (large distance with only one 4-stall station in Cheyenne), Pueblo to Raton (nearly 150 miles, only one stop in Colorado City and one Tesla-only site in Trinidad), and Raton to Santa Fe (125 miles of nothing fast)
“Local tow companies report rescuing ~2–3 stranded EVs per week in the Raton/Las Vegas area.”
Tier III–IV modular data hall serving regional clients.
On‑site solar canopy and battery storage for resilient power.
4–6 DC fast chargers with V2G capability; leverages data center power infrastructure.
Provides high‑tech jobs, broadband access and green mobility for Raton residents.
Digital Hubs are about agility, integration, and edge optimization, complementing the hyperscale nodes by handling data closer to where it’s needed and providing infrastructure (fiber, chargers, smart grid) to the local community.
Digital hubs are smaller modular 5–10 MW facilities that repurpose existing structures through adaptive reuse to create mini datacenters for colocating data, EV charging and battery storage on a single site
Adaptive reuse of vacant big‑box stores accelerates deployment and revitalizes communities.
Hyperscale data centers (>50 MW) remain concentrated in metro markets; hubs serve the edge and reduce latency and charging gaps between metro centers and boost power and computing capabilities
Raton keeps appearing with all the necessary elements for early success
City‑owned 115 kV substation provides ~20 MW today; scalable to 50 MW with upgrades.
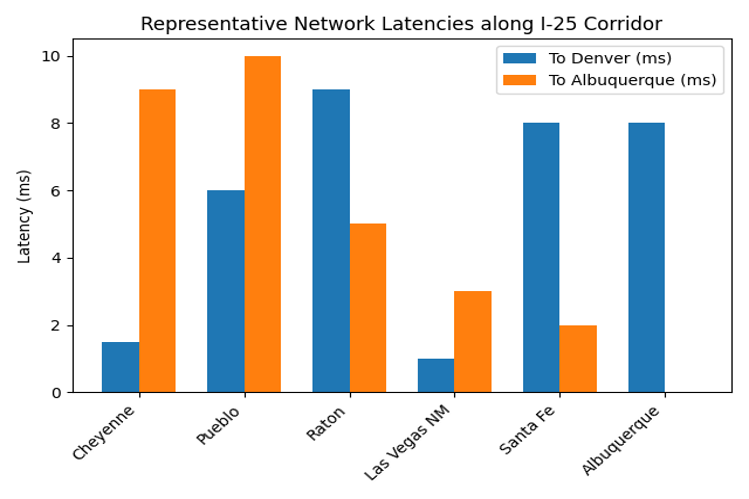
Central location fills a 125‑mile EV charging gap and offers <10 ms latency to Denver/ Dallas.
Cool climate (6,700 ft) reduces cooling loads; low-cost renewable power nearby.
Properties and assets readily available for immediate buildout and quicker uptime
Redevelops blighted Kmart and power plant sites consistent with the Comprehensive & Strategic Plans.
Expands broadband and EV infrastructure – addressing Comp Plan goals for connectivity & “dig once” fiber.
Cool climate Creates high‑wage jobs and vocational training aligned with the Economic Development Plan. (6,700 ft) reduces cooling loads; low-cost renewable power nearby.
Enhances downtown amenities (multi‑modal center chargers) per the Downtown Master Plan.
PHASE 1
PHASE 2
PHASE 3
Prepare airport industrial park for future 10–20 MW expansion and freight charging.
Finalize property acquisition for Kmart site and secure leases/rights for plant & airport parcels.
Engage utilities & engineers for Kmart site and secure leases/rights for plant & airport parcels.
Submit NEVI, CFI, and LEDA applications; coordinate IRB issuance with city council & bond counsel.
Initiate design-build RFP for Phase 1; integrate apprenticeship hiring plan with schools and trade unions.
Initiate design-build RFP for Phase 1; integrate apprenticeship hiring plan with schools and trade unions.

Retrofit the 40,327 sq ft former Kmart into a 5–10MW digital hub with an EV charging plaza.
Estimated conversion cost: $5–10MM (plus ~$600k property acquisition). Utilise Opportunity Zone, Industrial Revenue Bonds and LEDA grants.
Latency impact: <10ms to Denver/Dallas, ~4–6ms to Albuquerque; fills the I‑25 corridor latency gap.
ROI: Projected 10–15% unlevered return. ~\$8MM/year colocation revenue at 5MW; EV charging adds $50–100k/year, growing with adoption.

Become a Critical Intersection to the Growing Digital Railway
Redevelop the decommissioned coal plant and 115 kV substation into a 10–25 MW Tier IV data campus.
Costs: expansion to 25MW may aPhase 2 (~5–10MW) requires $30–50MM; dd another $40 M. Fund via Industrial Revenue Bonds, NM tax credits and federal grants.
Latency impact: Provides redundancy and additional capacity; ensures <5 ms connections to Albuquerque and Denver, enhancing regional resilience.
ROI: Long‑term leasing to hyperscalers yields ~12% IRR. Campus can earn $15–20MM/year at 10MW with complementary megacharger revenue.

Energy & Data Industrial Park for the Future
Designate 40+ acres near Crews Field for an Energy & Data Industrial Park supporting 20–50 MW of computing and storage.
Costs: $10–20 M for roads, utilities and fiber.
Future data hall costs TBD; financed through partnerships, federal grants and private capital.
Latency impact: Extends edge coverage east–west, keeping latency <5 ms across rural New Mexico and linking to Texas corridors.
ROI: Multi‑decade play targeting logistics, cloud and green‑energy tenants; incremental revenue from solar, batteries and truck charging.
Building Grid Resilience by returning power
Suggested Capital Stack mixing, grants, favorable loans, and investors
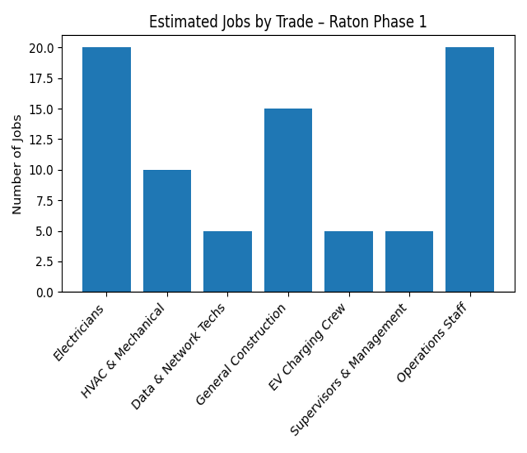
Phase 1: construction employs 50–70 workers;
Phase 2: employs 100+ workers at peak.
100+ workers
Structured, modular approach that is less capital intensive then traditional datacenter only buildouts
Structured, modular approach that is less capital intensive then traditional datacenter only buildouts
Suggested Capital Stack mixing, grants, favorable loans, and investors
Funding Source | Description | Potential Benefit |
NEVI Formula Program | Federal highway funds covering 80% of EV charger costs | ~$480k grant for 4 fast chargers |
LEDA & Rural Job Credits | State grants & credits rewarding job creation in rural areas | $1–2M grant; $4k credit per job & 8.5% wage refund |
Industrial Revenue Bonds | City-issued bonds exempt property & sales taxes | Saves 5–7% equipment cost & property tax for 20+ years |
New Markets & OZ | Federal programs for low-income & Opportunity Zones | Up to 39% project financing via NMTC; tax-free OZ appreciation |
USDA/EDA & CFI Grants | Rural broadband & clean energy grants including EV truck plazas | Potential multi-million funding for Phase 2 & freight charging |
Multiple Pathways to Successfully exit Investments
build, fill and stabilize the hub then sell to an infrastructure investor or REIT at premium.
develop and package the project early for sale to a data center or charging operator.
IRB and PILOT agreements transfer, ensuring Raton’s tax benefits remain intact.
Capital and Trade Partnerships built achieve success
In‑house electrical, HVAC and automation divisions enable self‑performing critical work.
Partnerships with top general contractors ensure timely construction and procurement.
Proven track record delivering smart campuses and data centers in the region.